info@skin4passion.com
IN&OUT HEALTHY SRL
Via Umbria 33, 57017 Collesalvetti (LI) - Italy
Ufficio Commerciale
Via Monte Napoleone 8, 20121 Milano (MI) - Italy
The Skin4Passion range of products are natural and dermatologically tested products. Their application endows the skin with softness, glow, nourishment and elasticity.
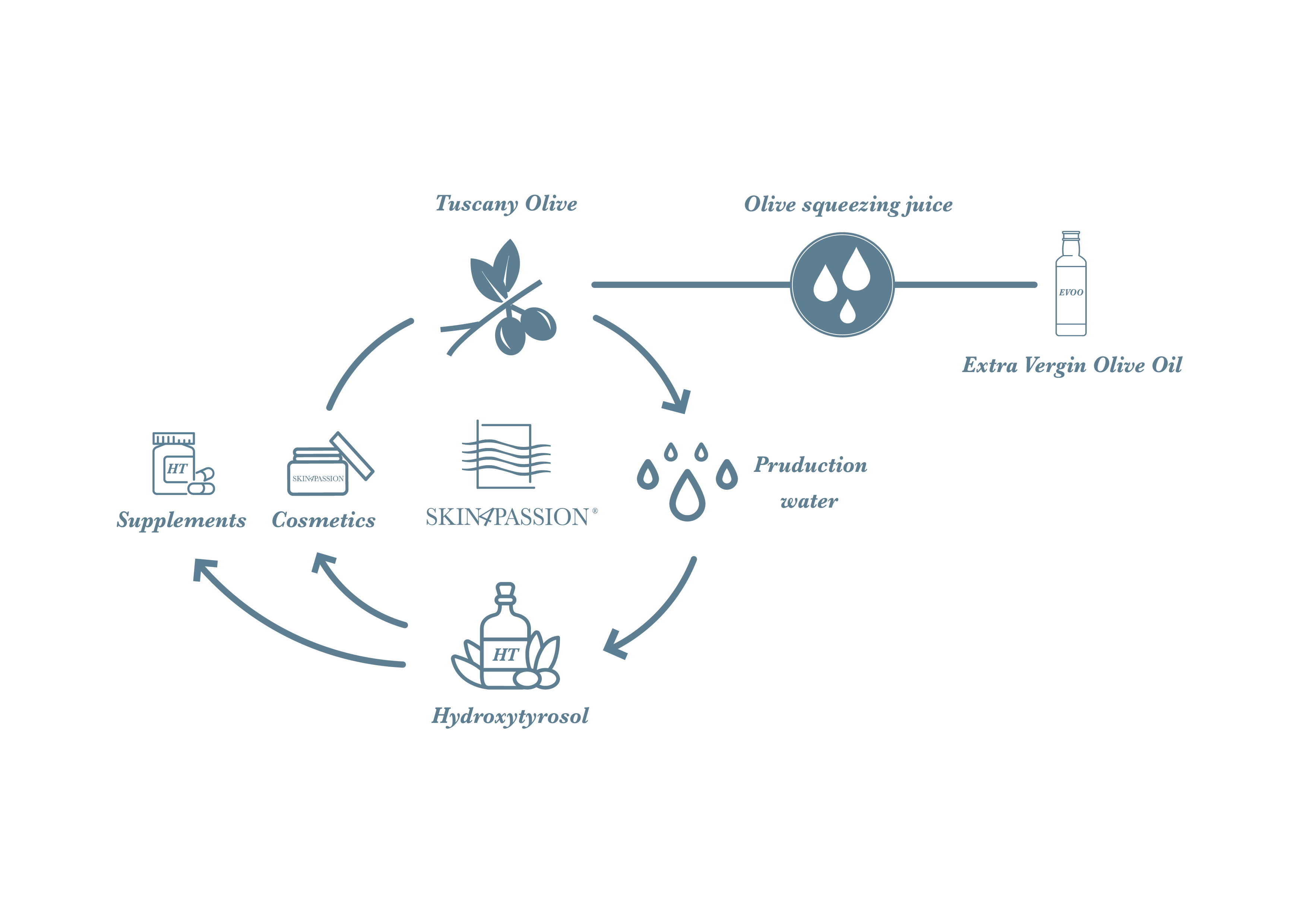
Skin4Passion opts for the use of hydroxytyrosol, a polyphenol found naturally in olives, as a natural and functional active ingredient.
Hydroxytyrosol is a polyphenol typically produced by the olive tree (Olea europaea L.). The remarkable antioxidant properties of hydroxytyrosol are based on its ability to interact with specific “targets” in our body and, through them, to activate our endogenous “antioxidant machinery”. In other words, hydroxytyrosol promotes and awakens our natural endogenous antioxidant defences, which risk becoming weakened over time.
Polyphenols are natural organic substances produced as “secondary metabolites” by many plant species. Polyphenols are recognised as offering useful biological properties with key importance in various areas such as cosmetics or nutraceuticals. Among their most important “widespread” biological properties are their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions to protect the cells of our body against oxidative stress.
Nowadays, it is essential to stay connected, and this leads us to use our devices more and more. Smartphone, computer or tablet screens are our windows into the world and mirrors of ourselves.
Skin4Passion has decided to use natural and functional active ingredients such as hydroxytyrosol, which, according to a study* published in June 2019 in the Journal of Cellular Physiology, offers a prevention activity on human keratinocytes and fibroblasts from damage due to exposure to blue light radiation on the skin, and thus helps protect against the Blue Light of our screens.
Reference*: R. Avola, A.C.E. Graziano, G. Pannuzzo, F. Bonina, V. Cardile: Hydroxytyrosol from olive fruits prevents blue-light-induced damage in human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun; 234(6): 9065-9076. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cookie Shop | 1 month | Cookie necessary for the Online Shop to function properly |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics-2 | 1 year | This cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin to store user consent for cookies in the "Analytics" category. |
| PHPSESSID | Session | This cookie is native to PHP applications. The cookie is used to store and identify a user's unique session ID for the purpose of managing the user's session on the website. The cookie is a session cookie and is deleted when all browser windows are closed. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _gat - Google Analytics | 1 minute | This cookie is installed by Google Universal Analytics to limit the request rate and therefore limit the collection of data on high traffic sites. |
| _gid - Google Analytics | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, the _gid cookie stores information about how visitors use a website, also creating an analytical report of the website's performance. Some of the data that is collected includes the number of visitors, their origin and the pages they visit. anonymously. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _fbp - Facebook Pixel | 3 months | This cookie is set by Facebook to display advertisements on Facebook or on a digital platform powered by Facebook advertising, after visiting the website. |
| fr - Facebook Pixel | 3 months | Facebook sets this cookie to show relevant advertisements to users by monitoring user behavior on the web, on sites that have Facebook pixels or Facebook social plug-ins. |